1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
| # app.py
import os
import sys
sys.path.append("./")
import torch
from src.transformer import Transformer2DModel
from src.pipeline import Pipeline
from src.scheduler import Scheduler
from transformers import (
CLIPTextModelWithProjection,
CLIPTokenizer,
)
from diffusers import VQModel
import gradio as gr
# 运行环境
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 模型文件目录
model_path = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), 'ModelSpace', 'MeissonFlow', 'Meissonic')
# 模型初始化
model = Transformer2DModel.from_pretrained(model_path, local_files_only=True, subfolder="transformer")
vq_model = VQModel.from_pretrained(model_path, local_files_only=True, subfolder="vqvae")
text_encoder = CLIPTextModelWithProjection.from_pretrained(model_path, local_files_only=True, subfolder="text_encoder")
tokenizer = CLIPTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, local_files_only=True, subfolder="tokenizer")
scheduler = Scheduler.from_pretrained(model_path, local_files_only=True, subfolder="scheduler")
pipe = Pipeline(vq_model, tokenizer=tokenizer, text_encoder=text_encoder, transformer=model, scheduler=scheduler)
pipe.to(device)
MAX_SEED = 2 ** 32 - 1
MAX_IMAGE_SIZE = 1024
def generate_image(prompt, negative_prompt, seed, randomize_seed, width, height, guidance_scale, num_inference_steps,
progress=gr.Progress(track_tqdm=True)):
if randomize_seed or seed == 0:
seed = torch.randint(0, MAX_SEED, (1,)).item()
torch.manual_seed(seed)
image = pipe(
prompt=prompt,
negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
height=height,
width=width,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps=num_inference_steps
).images[0]
return image, seed
# Default negative prompt
default_negative_prompt = "worst quality, low quality, low res, blurry, distortion, watermark, logo, signature, text, jpeg artifacts, signature, sketch, duplicate, ugly, identifying mark"
css = """
#col-container {
margin: 0 auto;
max-width: 640px;
}
"""
examples = [
"Modern Architecture render with pleasing aesthetics.",
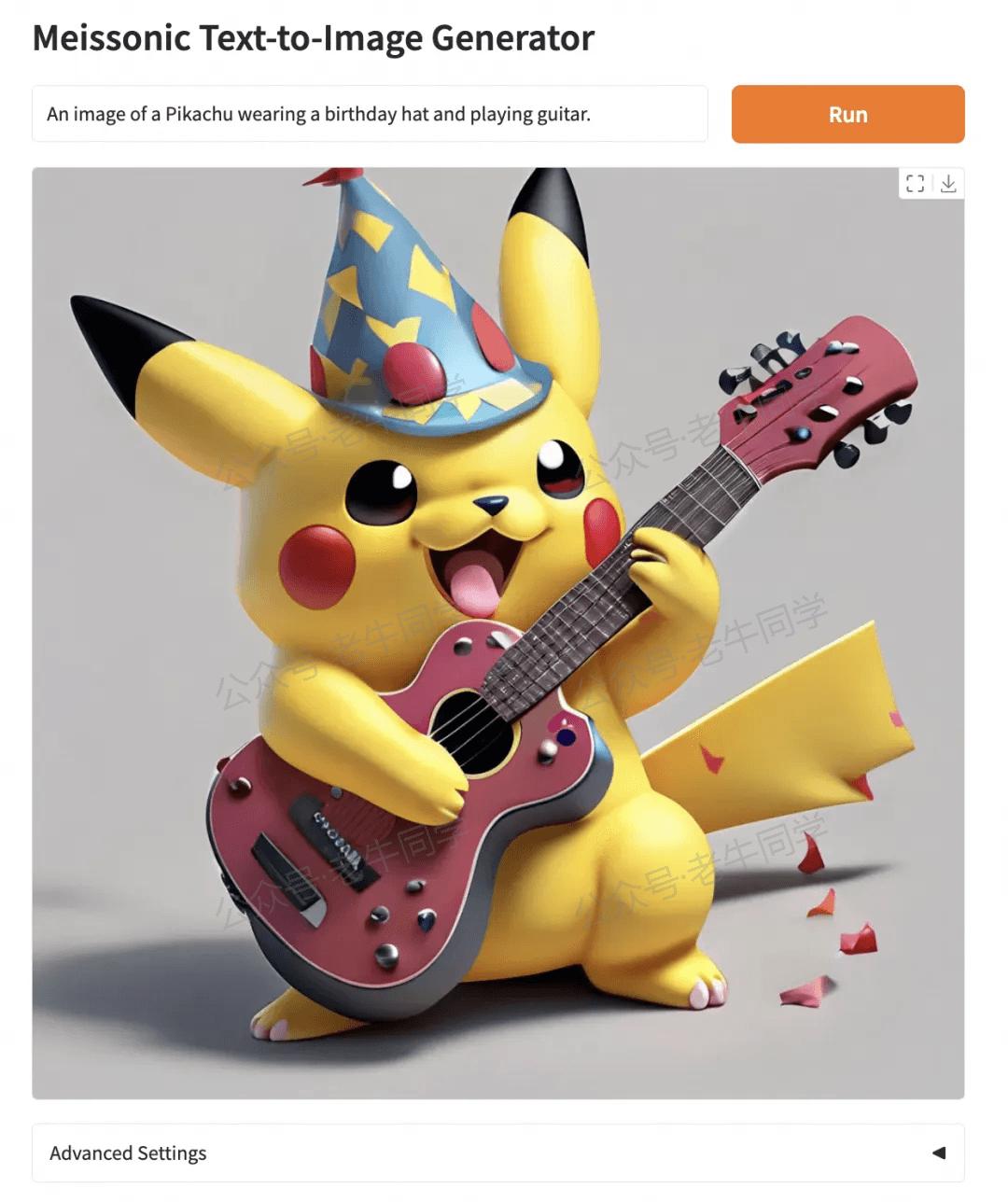
"An image of a Pikachu wearing a birthday hat and playing guitar.",
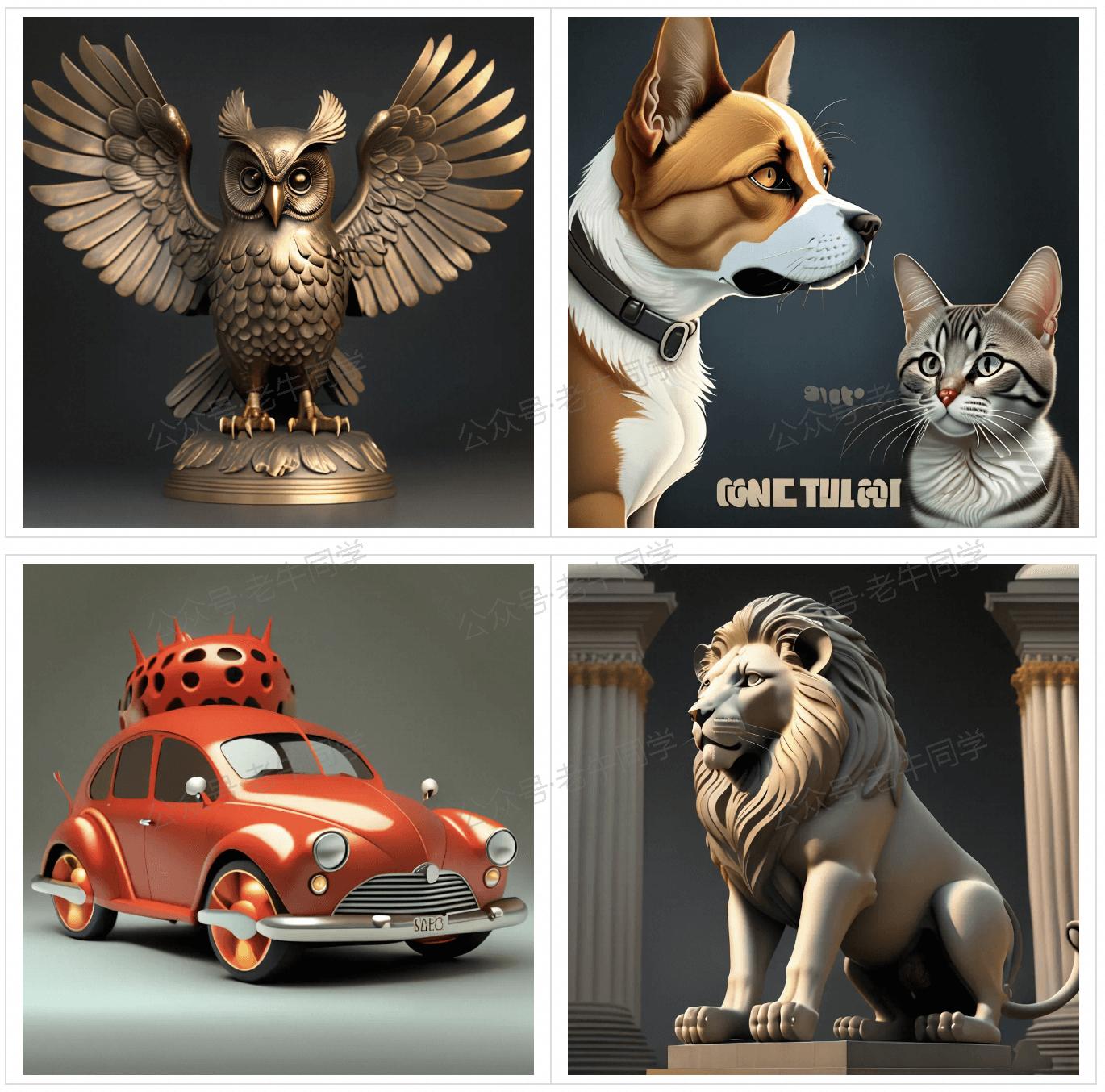
"A statue of a lion stands in front of a building.",
"A white and blue coffee mug with a picture of a man on it.",
"A metal sculpture of a deer with antlers.",
"A bronze statue of an owl with its wings spread.",
"A white table with a vase of flowers and a cup of coffee on top of it.",
"A woman stands on a dock in the fog.",
"A lion's head is shown in a grayscale image.",
"A sculpture of a Greek woman head with a headband and a head of hair."
]
with gr.Blocks(css=css) as demo:
with gr.Column(elem_id="col-container"):
gr.Markdown("# Meissonic Text-to-Image Generator")
with gr.Row():
prompt = gr.Text(
label="Prompt",
show_label=False,
max_lines=1,
placeholder="Enter your prompt",
container=False,
)
run_button = gr.Button("Run", scale=0, variant="primary")
result = gr.Image(label="Result", show_label=False)
with gr.Accordion("Advanced Settings", open=False):
negative_prompt = gr.Text(
label="Negative prompt",
max_lines=1,
placeholder="Enter a negative prompt",
value=default_negative_prompt,
)
seed = gr.Slider(
label="Seed",
minimum=0,
maximum=MAX_SEED,
step=1,
value=0,
)
randomize_seed = gr.Checkbox(label="Randomize seed", value=True)
with gr.Row():
width = gr.Slider(
label="Width",
minimum=256,
maximum=MAX_IMAGE_SIZE,
step=32,
value=1024,
)
height = gr.Slider(
label="Height",
minimum=256,
maximum=MAX_IMAGE_SIZE,
step=32,
value=1024,
)
with gr.Row():
guidance_scale = gr.Slider(
label="Guidance scale",
minimum=0.0,
maximum=20.0,
step=0.1,
value=9.0,
)
num_inference_steps = gr.Slider(
label="Number of inference steps",
minimum=1,
maximum=100,
step=1,
value=64,
)
gr.Examples(examples=examples, inputs=[prompt])
gr.on(
triggers=[run_button.click, prompt.submit],
fn=generate_image,
inputs=[
prompt,
negative_prompt,
seed,
randomize_seed,
width,
height,
guidance_scale,
num_inference_steps,
],
outputs=[result, seed],
)
# 启动WebUI界面
demo.launch()
|